Assessment of Role of Dopamine in Medial Amygdala on Body Weight, Metabolic Profile and Lipid Risk Factors in Albino Wistar Rats
Abstract
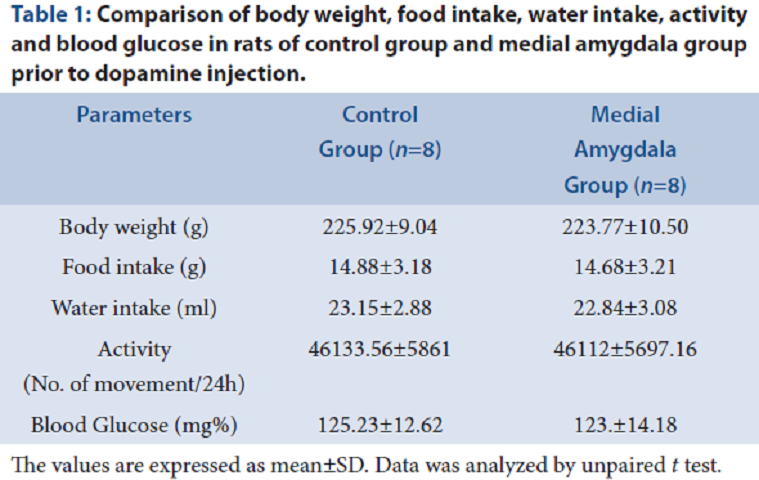
Background and Aim: The present study was conducted to assess the role of dopamine in amygdala in the body weight, blood glucose, lipid profile and lipid risk factors in albino Wistar rats. Methods: A total of 16 albino Wistar rats were taken for the study and were divided into medial amygdalar group and control group with 8 rats in each group. Stereotaxic cannulation was performed and dopamine was injected into the medial amygdalar nuclei. Blood sample was obtained for estimation of metabolic parameters (blood glucose and lipid parameters) before and after dopamine injection, by computerized metabometer and autoanalyzer. Results: Following dopamine injection, there was decrease in body weight, blood glucose, lipid profile and lipid risk factors in medial amygdala group compared to control group. There was positive correlation of body weight with blood glucose, triglyceride, very low-density lipoprotein and atherogenic index. Conclusion: Decrease in body weight, blood glucose, lipid profile and lipid risk factors induced by dopamine in medial amygdalar group could be linked to reduction in cardiometabolic risks in these rats. Reduction in body weight could be the key element in inducing reduction of cardiometabolic risks.