Assessment of Heart Rate Variability in Early Post-menopausal Women
Abstract
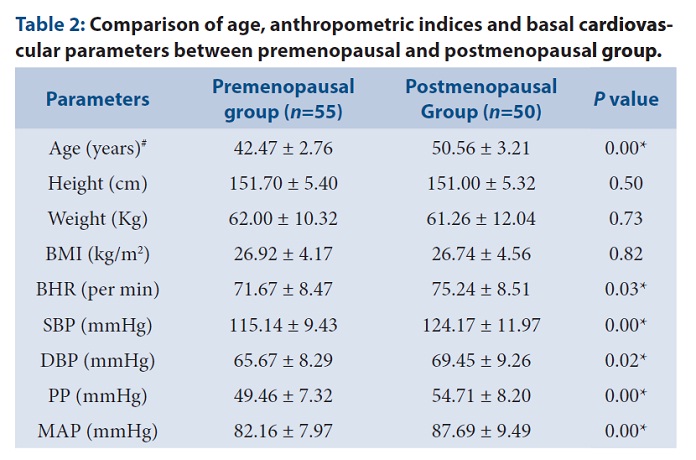
Background and Aim: Menopause marks to a point in time that follows after the permanent stoppage of menstruation. Menopausal transition includes various autonomic dysfunctions. Age is known to affect autonomic function. Therefore, in the present study the effect of menopause on autonomic function has been assessed by comparing the heart rate variability parameters between early postmenopausal and late premenopausal women. Methods: Premenopausal and postmenopausal women of age group between 40-55 years were recruited and short term HRV was measured using BIOPAC and analysed with kubios software. Results: In postmenopausal women, HFnu was significantly reduced, LFnu, LF: HF ratio were significantly increased and among the time domain parameters, RMSSD was significantly reduced in postmenopausal women. Conclusion: Sympathovagal imbalance in the form of increased sympathetic and decreased parasympathetic activity was found in early postmenopausal women. There was considerable decrease in vagal indices in postmenopausal women which is known to increase cardiovascular risks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





