Correlation of Smoking Index with Mid-expiratory Flow Rate in Tobacco Smokers
Abstract
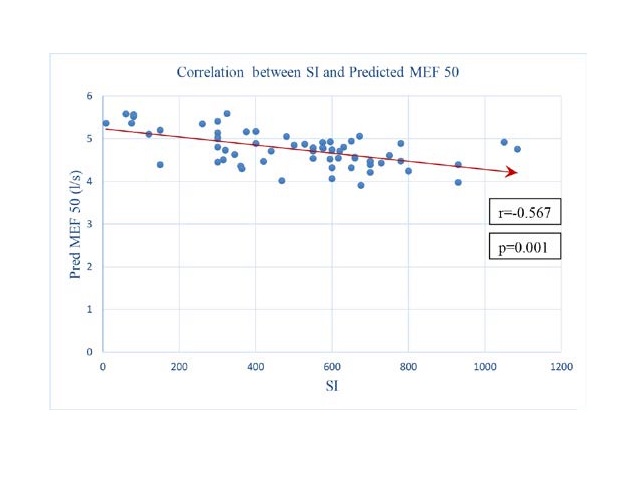
Background and Aim: Tobacco smoking was injurious to health, lung function and cause for many diseases has been known to mankind since decades. Access, peer pleasure, and various causes lead to addiction to tobacco smoking, and leads to a morbid lifestyle in later life. The aim of the study was to find out the harmful impact of the tobacco smoke on lung health by comparing the effect of the exposure of tobacco smoke on the mid-expiratory lung function indices (MEF75, MEF50, and MEF25). Methods: The study was carried out on 80 subjects between the age group of 18 - 45 years, and were divided into two groups with 40 subjects in tobacco smokers’ and 40 subjects as controls, and PFT indices were obtained before and after giving bronchodilator. Smoking index was calculated. Results: Predicted MEF25 and MEF75 were significantly decreased in tobacco smokers compared to control group. Predicted MEFR was significantly correlated with smoking index. Conclusion: Mid-Expiratory flow rate 25-75% was reduced in chronic smokers. The rate of reduction in MEFR 25-75% is proportional to the number of years the person been smoking.