The Experimental Study on the Alterations of Hemodynamics and Mechanical Characteristics of Erythrocyte Membrane after Different Training
Abstract
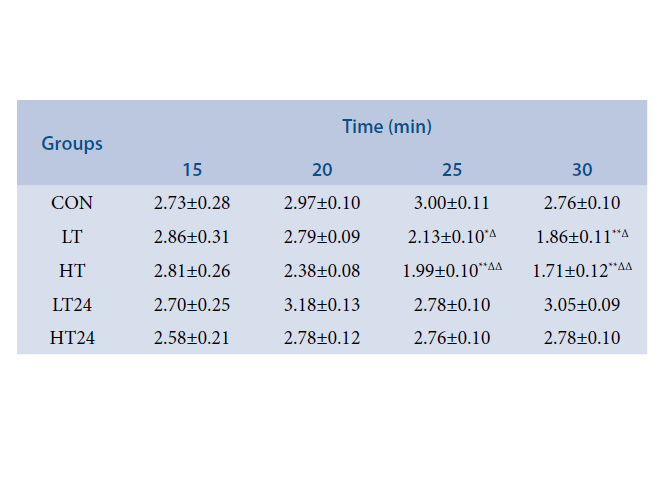
Background and Aim: The effect on erythrocyte membrane after different training and recovery, by evaluating relationship between the changes of mechanical characteristics of erythrocyte membrane and hemodynamic indices was assessed. Methods: The Sprague Dawley rats were divided into 5 groups (n=7). The rats were trained on treadmill for four weeks, six days per week except for control group that stayed sedentary. The effect of training on hematocrit and mechanical characteristics of the erythrocyte membrane (elasticity and interaction energy) by using dielectrical electrophoresis and the mathematical model were assessed. Results: Training for 3 weeks improved hematocrit and mechanical characteristics after recovery and elasticity and interaction energy in RBC membrane decreased transitorily at different levels after high intensity training. Conclusion: The effect of training in RBC mechanical characteristics is that changes of RBC membrane protein after high-intensity training cause the changes in RBC membrane structure and hence changes hemodynamics.