Investigation of the Effect and Possible Mechanism of Antihypertensive Activity of Lycopene-rich Extract of Solanum lycopersicon in Wistar Rats
Abstract
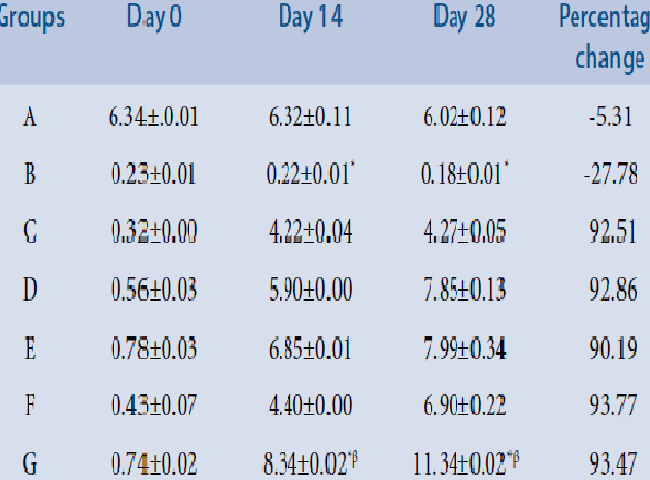
Background and Aim: Hypertension is a common debilitating illness among people in both developed and developing countries. This study investigated the effect and possible mechanism of the antihypertensive activity of lycopene-rich extract of Solanum lycopersicon (LRESL) on Wistar rats. Methods: Sixty hypertensive Wistar rats were divided into seven experimental groups viz: Group A served as a normotensive group and received food and clean distilled water ad libitum. Group B was the hypertensive untreated group; Groups C-E served as hypertensive group administered with 100, 200, and 400 mg/kg LRESL, respectively. While group F was hypertensive and received 10 mg/kg amlodipine and group G received 200 mg/kg of LRESL+0.5 mg/kg Lisinopril respectively. Results: There was a statistical significant decrease (P<0.05) in the systolic and diastolic blood pressure and the decrease was in a dose-dependent manner. The heart rate showed no statistical significant difference among the groups. The total cholesterol (TC) increased in the positive and normal control compared to other groups. There was a significant decrease in the triglyceride (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in all hypertensive treated groups. The decrease in the LRESL treated groups was in a dose-dependent manner and there was no significant difference between the groups compared to the normotensive and positive control. Moreover, the high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) had a significant reverse effect of the LDL-C as there was a significant increase (P<0.05) in HDL-C and the increase was more significant in group E and G respectively. The serum cardiac arginase (SCAr) activity also decreased significantly (P<0.05) in all groups except group B compared to the normotensive and positive control groups and in a dose-dependent manner. The serum nitric oxide (SNO) concentration also increased in all test groups in a dose-dependent pattern except the positive control group. Conclusion: This study suggests that LRESL has an antihypertensive property and elicited this through multiple mechanisms involving a decrease in SCAr, LDL-C, body weight and marked elevation of SNO and could be used as a novel compound channeled into the production of antihypertensive drugs.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





