Ameliorative Effects of EUK-134, a Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase Mimetic, in a Rat Model of D-Galactose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Accelerated Aging
Abstract
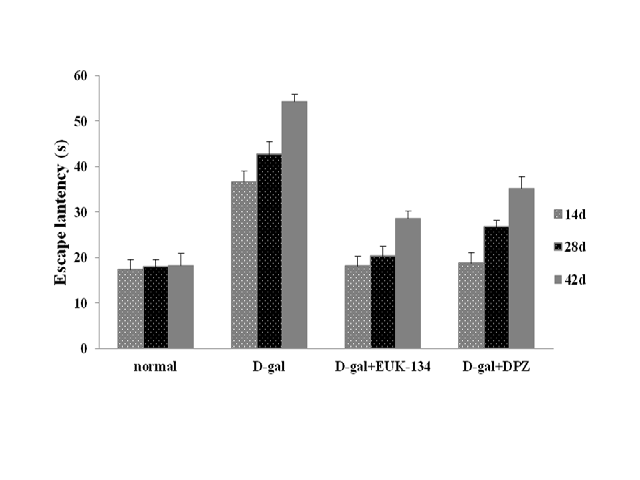
Background and Aim: EUK-134, a synthetic superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic, is a salen-manganese complex that exhibits the catalytic actions of both superoxide dismutase and catalase, important antioxidant enzymes biosynthesized by cells. In the current study, we evaluated the protection effects of EUK-134 against D-galactose-induced oxidative stress and accelerated aging in rats. Methods: D-galactose was sub-cutaneously injected at a dose of 100 mg/kg on the back of rats once daily for 42 days and simultaneously EUK-134 was administered to the rats by intra-abdominal injection at a dose of 5 mg/kg once daily. As a positive control, donepezil was administered to the rats by oral feeding at a dose of 1 mg/ kg once daily. Following behavioral tests (eight-arm radial maze test and Morris water maze test), animals were sacrificed on day 42, and their brains were used for histopathological and biochemical assessments of oxidative stress. Results: We found that the administration of EUK-134 (5 mg/kg, i.a.) significantly reversed the spatial memory deficits, the brain weight loss, the reduced cerebral cortex thickness, the decreased pyramidal neuron density and the pyramidal layer in brain hippocampus, the decreased superoxide dismutase activity, the decreased catalase activity, the increased malondialdehyde level, the increased acetylcholine esterase activity and the decreased acetylcholine level in the brain hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of D-gal-induced aging rats, as did the administration of donepezil (1 mg/ kg, oral). Conclusion: These results indicated that EUK-134 possesses neuroprotective effects against D-galactose-induced senescence, probably due to its antioxidant enzyme activities and this shows the availability of EUK-134 in the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease.