Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Analogues and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitors on Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Male Albino Rats
Abstract
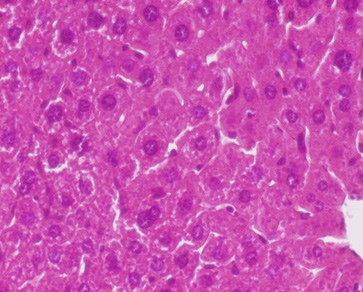
Background and Aim: Due to their importance in glucose metabolism and lipid accumulation, in addition to their prolonged action, overall safety and efficacy; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors (DPP-IV inhibitors) are becoming one of the cornerstones for treatment of obesity, T2DM and NASH. This study aimed to distinguish between the effect of both Liraglutide (a long-acting GLP-1 analog) and Sitagliptin (a DPP-IV inhibitor) on nutritional steatohepatitis in adult male rats. Methods: A total of 40 male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups; the normal control group and the steatohepatitis placebo group; steatohepatitis liraglutide- treated and steatohepatitis sitagliptin-treated groups. Liver weight and functions, lipid profile, glycemic status, hepatic oxidant-antioxidant parameters and histopathological analysis were assessed in comparison with the control rats. Results: Treatment of steatohepatitis in rats with either liraglutide or sitagliptin significantly reduced the levels of blood sugar, insulin, HOMA-IR, hepatic MDA and nitric oxide (NO). Moreover, they significantly increased the antioxidant enzyme activities, improved the histopathological changes compared to the control rats, with slightly superior effects for Liraglutide. Conclusion: Treatment with either GLP-1 RAs or DPP-IV inhibitors improved the hepatocyte viability. Treatment improved the hepatic fatty deposition, attenuated the progression of hepatic fibrosis and reduced the hepatic oxidative stress in male steatohepatitis rats, with slightly superior effects for GLP-1 RAs.