Evidence of Systemic Responses to Viral Pathogens using Malondialdehyde, Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and Superoxide Dismutase
Abstract
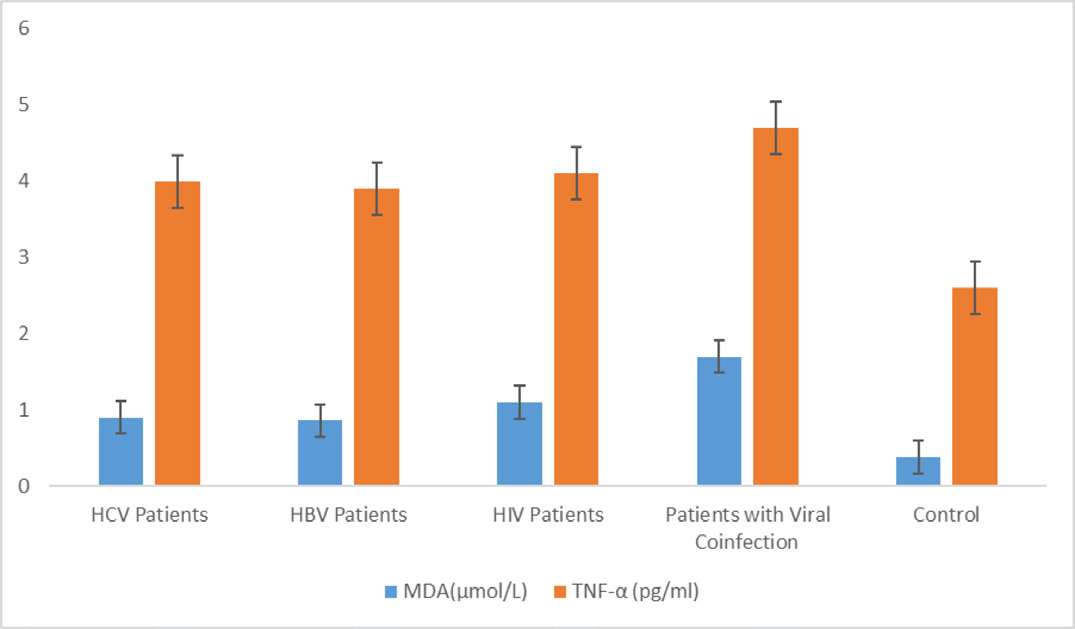
Background and Aim: Infectious agents are triggers of oxidative stress and inflammation. This work was designed to determine evidence of systemic responses to viral pathogens using malondialdehyde, tumor necrosis factor alpha and superoxide dismutase. Methods: The subjects recruited for this study include 23 HCV mono-infected volunteers (aged 24-67 years; Male-10; Female-13), 30 HBV mono-infected volunteers (aged 24-67 years; Male-15; Female-15), 18 HIV mono-infected volunteers (aged 24-67 years; Male-8; Female-10), 23 Viral (HCV, HIV, HBV) Co-infected volunteers (aged 24-67 years; Male-10; Female-13) and 50 age matched control volunteers who were not infected with HCV, HIV or HBV (Female-25; Male-25). Subjects tested negative to Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB) and Plasmodium tests were recruited. Test subjects who have not initiated antiviral therapy were recruited for the study. Five milliliters of venous blood was obtained from each of the subjects into lithium heparinized bottles for the assay of HCV, HIV, HBV, TNFα by ELISA, SOD, MDA by Colorimetry, Giemsa thick blood film staining for plasmodium while sputum samples were obtained from each of the subjects for Ziehl Neelsen staining for Acid Fast Bacilli(AFB). Results: There was a significant increase in plasma MDA and TNF α in patients with viral co-infection compared with control and patients with mono-infections of HCV, HBV and HIV (p<0.05). There was a significant decrease in plasma SOD in patients with viral co-infection compared with control and patients with mono-infection of HBV (p<0.05; Table 1, 2; Figure 1, 2). The result also showed a significantly lower plasma SOD in patients with viral co-infection, mono-infection of HIV, HCV and HBV than the results obtained in the control subjects (p<0.05). There was a significant increase in plasma TNF-α in patients with viral co-infection compared with control and patients with mono-infections of HCV, HIV and HBV (p<0.05). The result also showed a significantly higher plasma TNF-α in patients with viral co-infection, mono-infection of HIV, HCV and HBV than the results obtained in the control subjects (p<0.05). Conclusion: The work revealed a significant evidence of systemic responses to viral pathogens as indicated by increased plasma malondialdehyde, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and decreased plasma superoxide dismutase in viral mono and coinfections.